PPT Introduction to Beam Theory PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID209977
A circle consists of two semi-circles above and below the x x axis, so the moment of inertia of a semi-circle about a diameter on the x x axis is just half of the moment of inertia of a circle. The moment of inertia about the vertical centerline is the same. Ix = I¯y = πr4 8. (10.2.11) (10.2.11) I x = I ¯ y = π r 4 8.
Torsional Moment Of Inertia

Moment of inertia of beam cross section I: Geometric properties of 2D figures . First moment of area: Center of area Second moment of area Parallel axis theorem First moment of area Given an area A of any shape . A x3 x2 dA x2 x3 in the x. 2-x 3 plane (as is the case for the cross section of a beam), the first moments of area with respect to
Moment of Inertia of Cylinder JordyntinReynolds

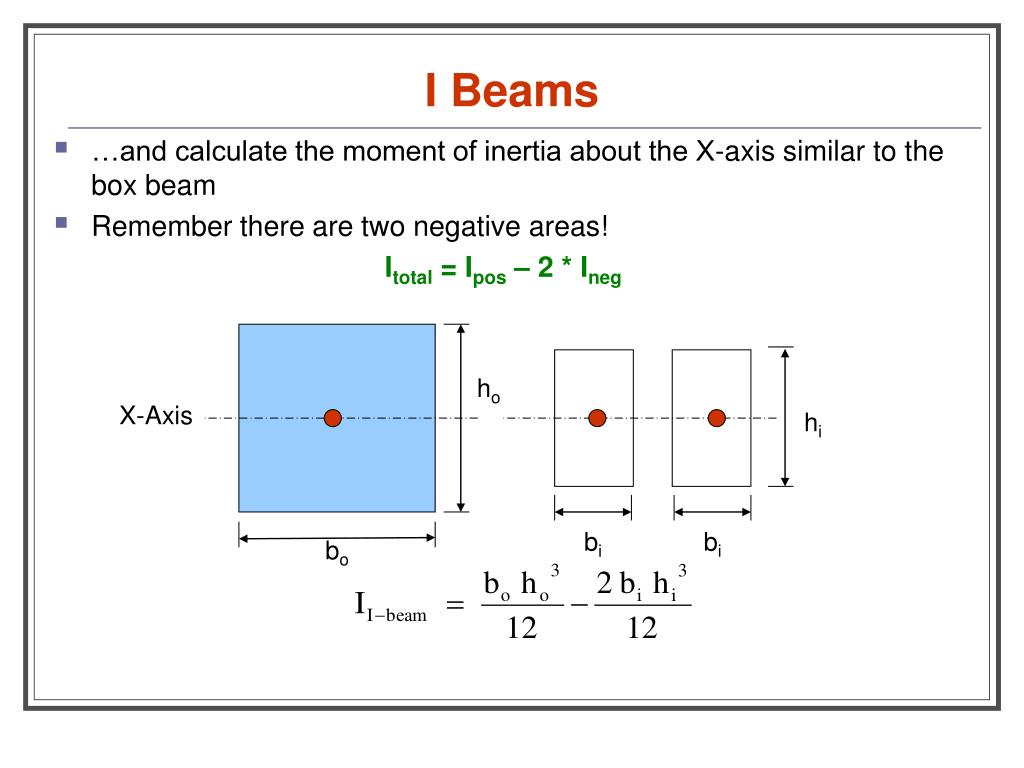
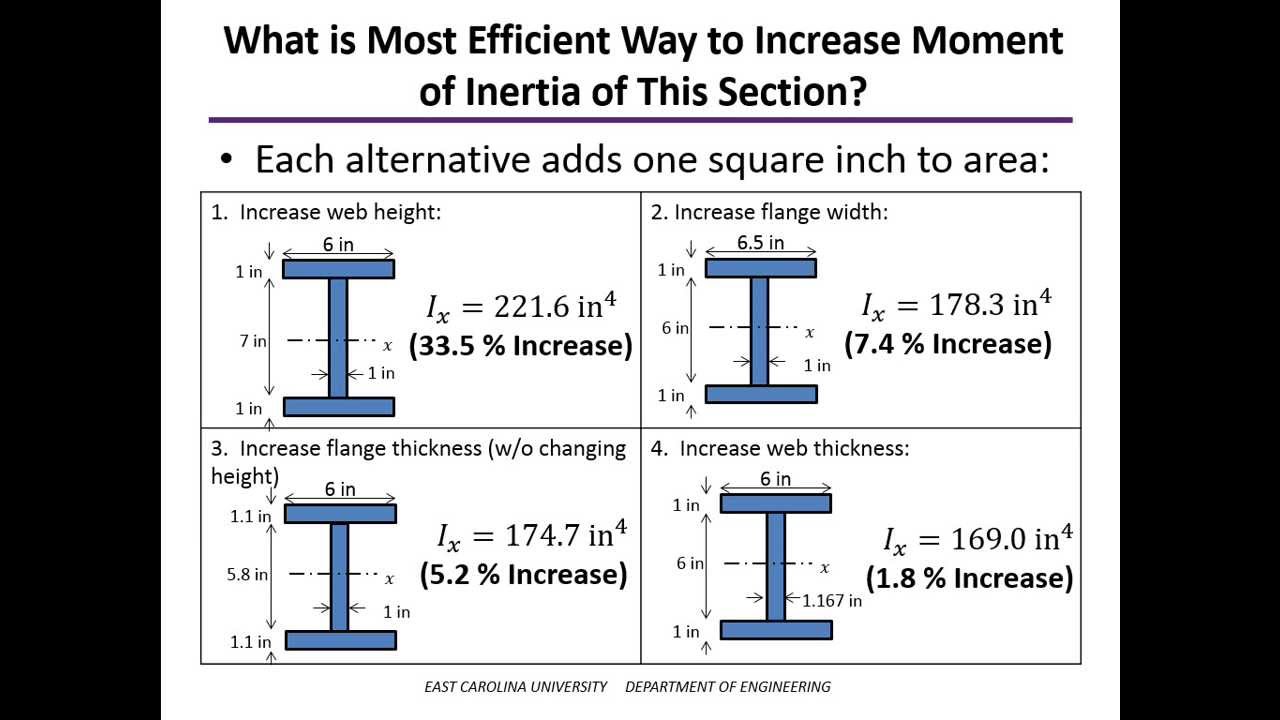
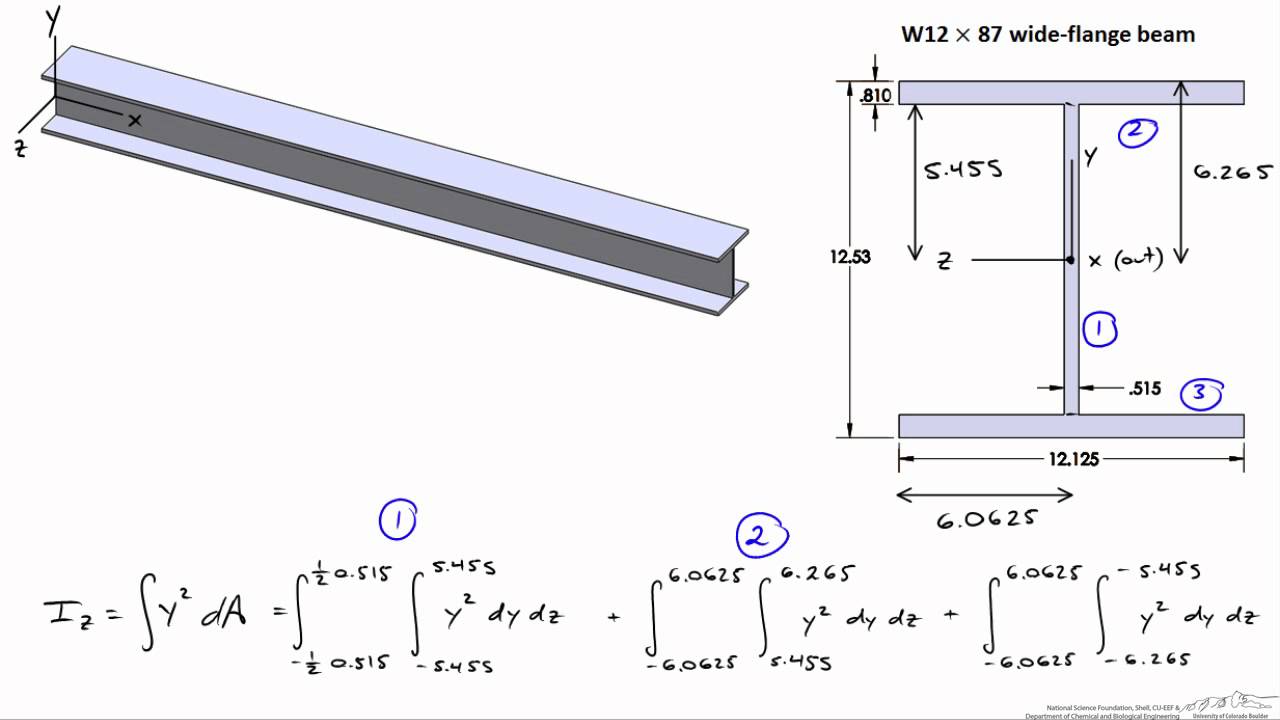
Step 1: Segment the beam section into parts. When calculating the area moment of inertia, we must calculate the moment of inertia of smaller segments. Try to break them into simple rectangular sections. For instance, consider the I-beam section below, which was also featured in our centroid tutorial. We have chosen to split this section into 3.
Moment of Inertia Examples YouTube
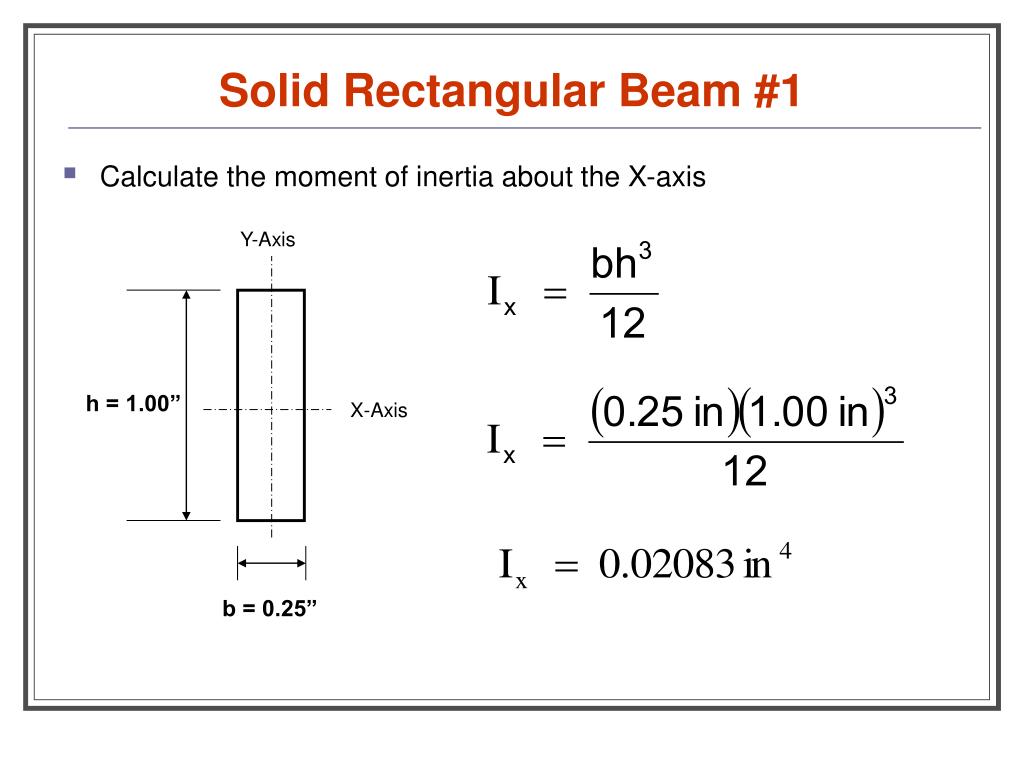
Area Moment of Inertia or Moment of Inertia for an Area - also known as Second Moment of Area - I, is a property of shape that is used to predict deflection, bending and stress in beams.. Area Moment of Inertia - Imperial units. inches 4; Area Moment of Inertia - Metric units. mm 4; cm 4; m 4; Converting between Units. 1 cm 4 = 10-8 m 4 = 10 4 mm 4; 1 in 4 = 4.16x10 5 mm 4 = 41.6 cm 4.
beam moment of inertia Google Search Engineering Notes, Engineering Student, Structural

The moment of inertia, otherwise known as the mass moment of inertia, angular/rotational mass, second moment of mass, or most accurately, rotational inertia, of a rigid body is a quantity that determines the torque needed for a desired angular acceleration about a rotational axis, akin to how mass determines the force needed for a desired acceleration..
Area Moment of Inertia Sistemas estruturais, Engenharia e construção, Engenharia civil

cross-sectional moment of inertia; moment of inertia of a beam; The second moment of area (moment of inertia) is meaningful only when an axis of rotation is defined. Often though, one may use the term "moment of inertia of circle", missing to specify an axis. In such cases, an axis passing through the centroid of the shape is probably implied..
Area Moment of Inertia of a WideFlange Beam YouTube
This tool calculates the moment of inertia I (second moment of area) of an I/H section (also called W-beam or double-T). The flanges are assumed equal. Enter the shape dimensions h, b, t f and t w below. The calculated results will have the same units as your input. Please use consistent units for any input.
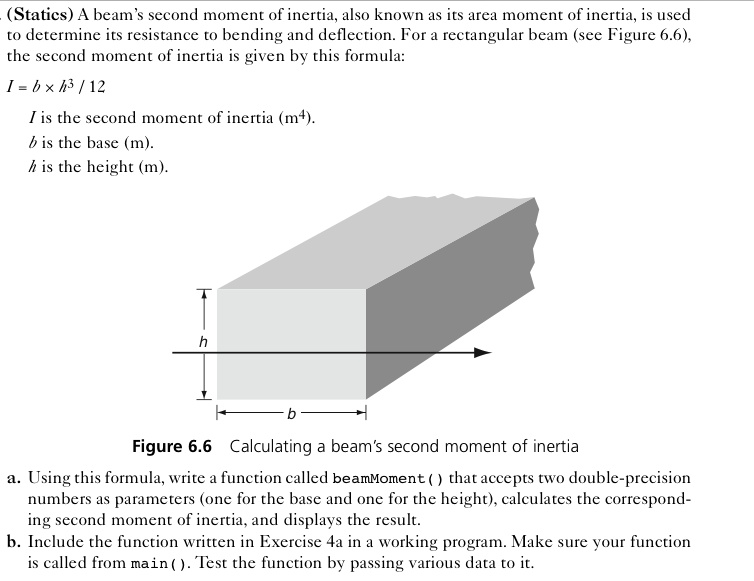
SOLVED using C++ programing method (Statics) A beam's second moment of inertia, also known as
Moment of Inertia. We defined the moment of inertia I of an object to be [latex]I=\sum _{i}{m}_{i}{r}_{i}^{2}[/latex] for all the point masses that make up the object. Because r is the distance to the axis of rotation from each piece of mass that makes up the object, the moment of inertia for any object depends on the chosen axis. To see this, let's take a simple example of two masses at the.
Second Moment Of Inertia For T Beam The Best Picture Of Beam
IntroductionNotations Relative to "Shear and Moment Diagrams". E= modulus of elasticity, psi. I= moment of inertia, in.4. L= span length of the bending member, ft. R = span length of the bending member, in. M= maximum bending moment, in.-lbs. P= total concentrated load, lbs. R= reaction load at bearing point, lbs. V= shear force, lbs.
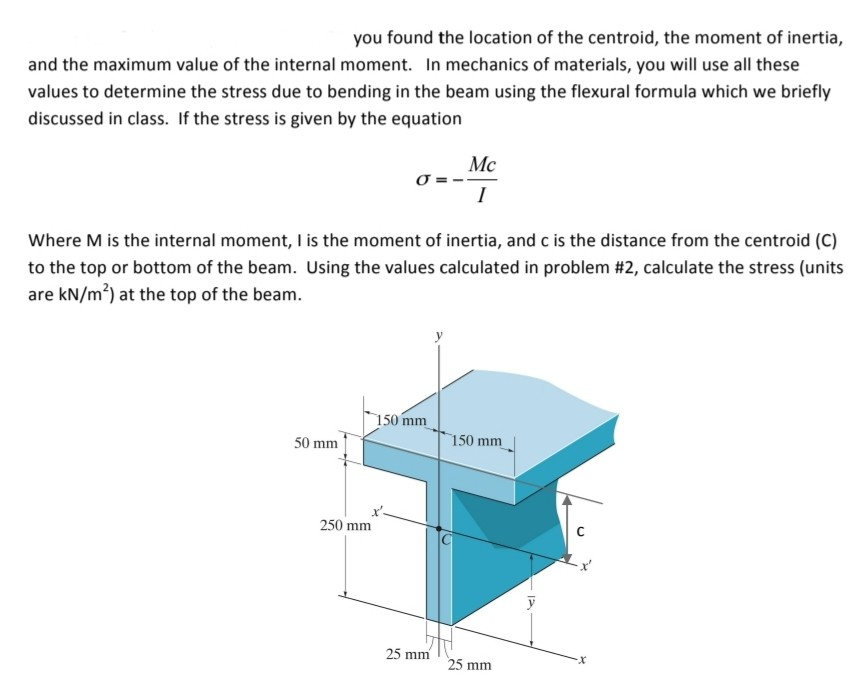
Determine the moment of inertia of the crosssectional area of the Tbeam with respect to the x

Example - Cantilever Beam with Single Load at the End, Metric Units. The maximum moment at the fixed end of a UB 305 x 127 x 42 beam steel flange cantilever beam 5000 mm long, with moment of inertia 8196 cm 4 (81960000 mm 4), modulus of elasticity 200 GPa (200000 N/mm 2) and with a single load 3000 N at the end can be calculated as. M max = (3000 N) (5000 mm) = 1.5 10 7 Nmm
Moment Of Inertia Formula Square Beam The Best Picture Of Beam
The moment of intertia of the first point is i1 = 0 (as the distance from the axis is 0). Of the second point: i2 = m (L/2)^2 = mL^2/4. Of the third point: i3 = mL^2. The total moment of inertia is just their sum (as we could see in the video): I = i1 + i2 + i3 = 0 + mL^2/4 + mL^2 = 5mL^2/4 = 5ML^2/12.
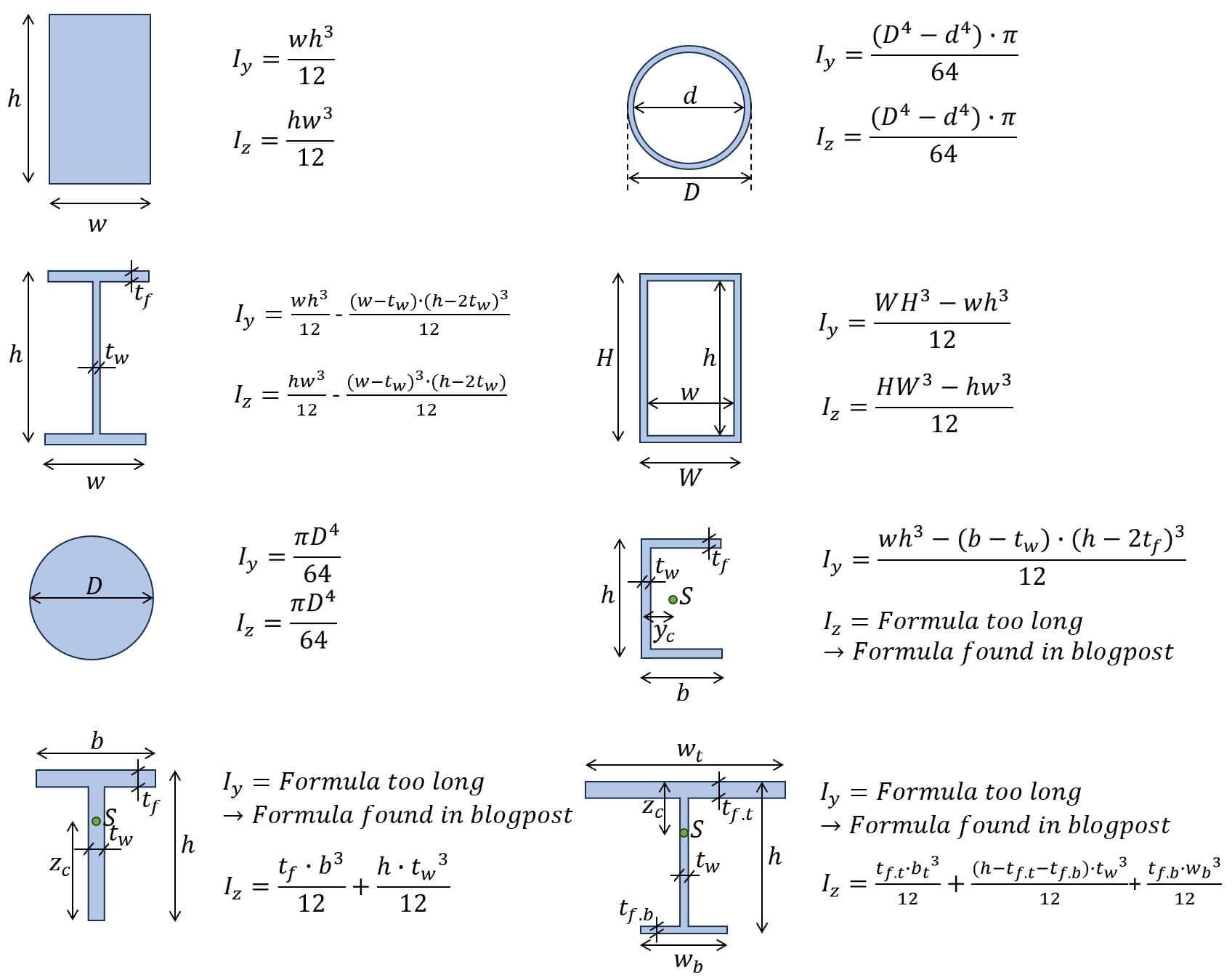
Moment Of Inertia Formulas For Different Shapes Structural Basics
The moment of inertia can be derived as getting the moment of inertia of the parts and applying the transfer formula: I = I 0 + Ad 2. We have a comprehensive article explaining the approach to solving the moment of inertia. Fundamentally, the moment of inertia is the second moment of area, which can be expressed as the following:
Mechanics of Materials Review of moment of inertia example YouTube

Formulas for Systems and Continuous Objects. For a rigid configuration of particles, the moment of inertia is simply the sum of all the individual moments. For a continuous distribution of mass, just as with the center of mass, we proceed by chopping the object into tiny elements of mass, and, for each element, add up the moment of inertia due.
Solved Find the moment of inertia to determine the maximum
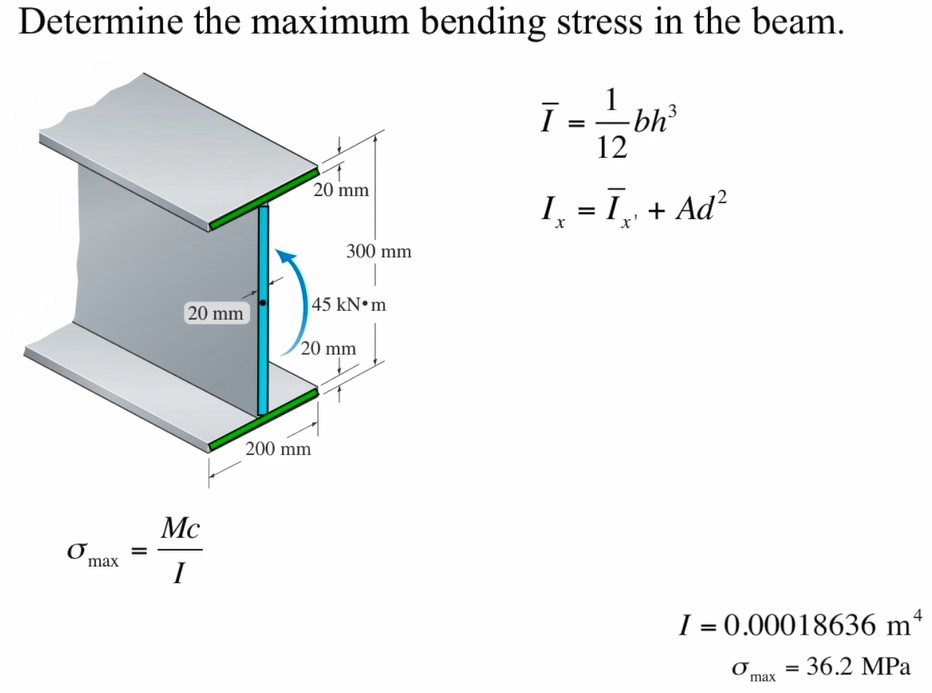
The moment of inertia of the area A with respect to the y-axis is given by Polar moment of inertia Moment of inertia is the property of a deformable body that determines the moment needed to obtain a desired curvature about an axis. Moment of inertia depends on the shape of the body and may be different around different axes of rotation. Moment.
Area Moment of Inertia in Beams YouTube

The moment of inertia about one end is 1 3 m L 2 1 3 m L 2, but the moment of inertia through the center of mass along its length is 1 12 m L 2 1 12 m L 2. Example 10.13 Angular Velocity of a Pendulum
Area Moment of Inertia (Beam Analysis and Design 1 a) YouTube

Figure 10.6.3: Calculation of the moment of inertia I for a uniform thin rod about an axis through the center of the rod. We define dm to be a small element of mass making up the rod. The moment of inertia integral is an integral over the mass distribution. However, we know how to integrate over space, not over mass.
.